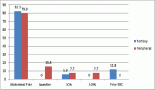
The prevalence of microsatellite instability and deoxyribonucleic acid mismatch repair deficiency in colorectal adenocarcinoma (CRC) cases is higher in India compared to western populations. No major study on the molecular pathogenesis is currently available in the Indian population. We conducted a pilot study to explore the differences in molecular pathogenesis of microsatellite stable (MSS) and microsatellite unstable CRC from a tertiary care centre in Kerala, South India. Using Nanostring PanCancer panel assay in Stage II colorectal adenocarcinoma, tumour tissues (n = 11) were compared against normal colon tissues (n = 4). Differentially expressed (DE) genes were identified and superimposed onto colon adenocarcinoma cohort of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data (TCGA Colon Adenocarcinoma (TCGA COAD)), from the Genome Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis and Tumor Immune Estimation Resource (TIMER) to compare the gene associations. Significant DE genes were 59 out of 730 (false discovery rate adj. p-value < 0.05), 18 of which had a fold-change |FC(log2)| ≥ 2. On superimposition to TCGA COAD, 33 genes were significant in both TCGA and current study. ETV4 was expressed significantly higher in MSS with no immune cell infiltration. Other significant DE genes with high FC(log2), unique to the study were INHBA, COL1A1, COL11A1, COMP, SFRP4 and SPP1, which were clustered in STRING network analysis and correlated with tumour-infiltrating immune cells in TIMER, suggesting a specific interaction pathway. The preliminary study suggests a distinct pathogenesis of MSS CRC involving ETV4 in the Indian population and warrants further clinically extensive and high-dimensional expression studies.