Purpose: Comorbidities have been indicated to influence cancer care and outcome, with strong associations between the presence of comorbidities and patient survival. The objective of this study is to determine the magnitude and pattern of comorbidities in Nigerian cancer populations, and demonstrate the use of comorbidity indices in predicting mortality/survival rates of cancer patients.
Methods: Using a retrospective study design, data were extracted from hospital reports of patients presenting for oncology care between January 2015 and December 2016 at two tertiary health facilities in Lagos, Nigeria. Patient comorbidities were ranked and weighted using the Charlson comorbidity index (CCI).
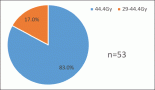
Results: The mean age for the 848 cancer patients identified was 53.9 ± 13.6 years, with 657 (77.5%) females and 191 (22.5%) males. Breast (50.1%), cervical (11.1%) and colorectal (6.3%) cancers occurred most frequently. Comorbidities were present in 228 (26.9%) patients, with the most common being hypertension (20.4%), diabetes (6.7%) and peptic ulcer disease (2.1%). Hypertension-augmented CCI scores were 0 (15.6%), 1–3 (62.1%), 4–6 (21.7%) and ≥7 (0.6%). The mean CCI scores of patients ≤50 years (0.8 ± 0.9) and ≥51 years (3.3 ± 1.2) were significantly different (p < 0.05). Patients with lower mean CCI scores were more likely to receive chemotherapy (2.2 ± 1.6 versus 2.5 ± 1.9; p < 0.05) and/or surgery (2.1 ± 1.5 versus 2.4 ± 1.7; p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Comorbidities occur significantly in Nigerian cancer patients and influence the prognosis, treatment outcome and survival rates of these patients. There is a need to routinely evaluate cancer patients for comorbidities with the aim of instituting appropriate multidisciplinary management measures where necessary.