Concerns about rising health care costs and the often incremental nature of improvements in health outcomes continue to fuel intense debates about ‘progress’ and ‘value’ in cancer research. In times of tightening fiscal constraints, it is increasingly important for patients and their representatives to define what constitutes ’value’ to them. It is clear that diverse stakeholders have different priorities. Harmonisation of values may be neither possible nor desirable. Stakeholders lack tools to visualise or otherwise express these differences and to track progress in cancer treatments based on variable sets of values.
The Patient Access to Cancer care Excellence (PACE) Continuous Innovation Indicators are novel, scientifically rigorous progress trackers that employ a three-step process to quantify progress in cancer treatments: 1) mine the literature to determine the strength of the evidence supporting each treatment; 2) allow users to weight the analysis according to their priorities and values; and 3) calculate Evidence Scores (E-Scores), a novel measure to track progress, based on the strength of the evidence weighted by the assigned value.
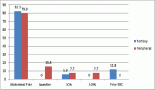
We herein introduce a novel, flexible value model, show how the values from the model can be used to weight the evidence from the scientific literature to obtain E-Scores, and illustrate how assigning different values to new treatments influences the E-Scores.
The Indicators allow users to learn how differing values lead to differing assessments of progress in cancer research and to check whether current incentives for innovation are aligned with their value model. By comparing E-Scores generated by this tool, users are able to visualise the relative pace of innovation across areas of cancer research and how stepwise innovation can contribute to substantial progress against cancer over time. Learning from experience and mapping current unmet needs will help to support a broad audience of stakeholders in their efforts to accelerate and maximise progress against cancer.