Background: To address the shortage of oncologists in the wake of the rapidly increasing global cancer burden, general practitioners of oncology (GPOs) have been added to cancer care teams worldwide. GPOs are family physicians with additional training in oncology and their roles differ by both country and region. In this study, we aimed to learn about the roles and expectations of GPOs from the perspective of oncologists in Canada and Nepal.
Methods: A survey was designed and administered to Canadian and Nepali Oncologists between February and November 2022 using Research Electronic Data Capture, a secure web-based software platform hosted at Queen’s University in Kingston, Ontario, Canada. Participants were recruited through personal networks/social media in Nepal and the survey was distributed through an email list provided by the Canadian Association of Medical Oncologists.
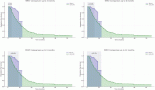
Results: The survey received 48 responses from Canadian and 7 responses from Nepali oncologists. Canadian respondents indicated that in terms of educational content delivery, clinics with oncologists followed by didactic lectures by oncologists were thought to be the most effective, followed by a small group learning and online education. Nepali oncologists also indicated didactic lectures by oncologists and small group learning would be the most effective teaching techniques, followed by online education and clinics with oncologists. Critical knowledge domains and skills most relevant for GPO training identified by Canadian respondents were managing pain and other common symptoms of cancers, as well as treatment of common side effects, followed by goals of care discussion, post-treatment surveillance for recurrence, and the management of long-term complications from treatment. Respondents from Nepal, however, suggested an approach to diagnosis to patient with increased risk of cancer, and cancer staging were the most critical knowledge domains and skills. The majority of oncologists in both countries thought a training program of 6–12 months was optimal.
Conclusion: We found many similarities in oncologist’s opinions of GPOs between the two countries, however, there were also some notable differences such as the need to provide cancer screening services in Nepal. This highlights the need to tailor GPO training programs based on local context.