Background: Cancer in young women is a major health problem in the Middle Eastern and North African population. We explored the awareness, barriers and practice of Arab oncologists towards oncofertility.
Methods: Oncologists from Arab countries treating female cancer patients were invited to complete a 30-item web-based questionnaire that explores oncologists’ demographics, available techniques and barriers to oncofertility.
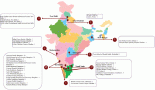
Results: 170 oncologists working in 9 different Arab countries responded to the questionnaire. Among the responders, 89 (52.4%) were from Egypt and the central region, 60 (35.3%) were from North Africa and 21 (12.4%) were from the Gulf region.
While most participants considered a dedicated training ‘necessary’, only 43 oncologists (25.3%) received a formal training. Only 17 participants (10%) had a fertility clinic in their centre, 44 (25.9%) and 13 (7.6%) had to refer patients to other centres or other cities, respectively. A total of 96 oncologists (56.5%) did not have access to a fertility preservation service.
Out of 147 responders, 79 (53.7%) offered fertility preservation only in patients presenting with early disease and 38 (25.9%) did not offer fertility preservation. In terms of proposed strategies, 50 responders (29.4%) offered embryo cryopreservation, 79 (46.5%) oocyte cryopreservation and 48 (28.2%) ovarian tissue cryopreservation.
Conclusion: A large gap exists between international clinical practice guidelines and current practices of fertility preservation in Arab countries. Barriers to optimum service delivery include the lack of physician awareness/training, unavailability of some advanced techniques and a lack of dedicated fertility clinics within the cancer centres.