Introduction: Glioblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumour in adults. Among all gliomas, it is the most aggressive type, with a high fatality rate, and according to the WHO classification, it is a grade IV tumour. As this tumour is well-known for its poor survival, an understanding of clinical and treatment-related prognostic factors can help in tailored treatment. The aim of this study was to know the impact of prognostic factors on survival in these cases.
Materials and methods: All glioblastoma patients treated in our hospital during 2010–2015 were included in the analysis. Cases were divided into different groups based on prognostic factors. Overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) were calculated and compared among the different groups. Statistical analysis was carried out using SPSS software v20.
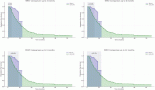
Results: One-year OS was 36.9% and 2-year OS was 10.8%. One-year DFS was 13.04%. On univariate analysis, age at presentation ≤45 years and adjuvant chemotherapy with six cycles or more temozolomide improved OS and DFS. Multivariate analysis retained the statistically significant positive impact of usage of adjuvant temozolomide chemotherapy of ≥six cycles on OS and DFS. The use of the anti-epileptic drug Levetiracetam had a statistically significant improvement of DFS.
Conclusion: Among various clinical and treatment-related prognostic factors evaluated in our study, younger age at presentation and addition of temozolomide chemotherapy to radiation showed improvement in OS and DFS. The use of the anti-epileptic drug Levetiracetam had an impact on DFS in glioblastoma patients.