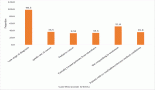
Thyroid and breast cancer are the most common cancers among young women, which are either synchronous or metachronous, but the association is yet to be elucidated. With the improvement of diagnosis and treatment, there is an increase in breast and thyroid cancer survivors. Hence, attention is shifting towards survivorship. Here, we report the case of a young lady diagnosed with synchronous thyroid and breast cancer who unexpectedly became pregnant during tamoxifen treatment. After a multidisciplinary discussion, endocrine therapy was interrupted and she delivered a healthy baby at term. In conclusion, oncologists should be aware of breast and thyroid cancer co-occurrence and examinations should be conducted together in diagnosis and follow-up. Also, pregnancy is feasible and can be considered after synchronous breast and thyroid cancer diagnosis. Physicians need to emphasise the use of barrier contraceptives to patients undergoing endocrine therapy. However, the optimum timing for pregnancy after breast cancer and the safety of endocrine therapy interruption in hormonal-positive patients should be discussed and managed by a multidisciplinary team.