Objective: This study aimed to compare lung cancer incidence, hospitalisation and mortality rates among municipalities of Rio Grande do Sul from 2000 to 2021 based on estimated radon gas exposure.
Methods: An ecological time series study was conducted using data from the Brazilian Geological Survey and the Ministry of Health. Geoprocessing techniques and Prais-Winsten regression were employed for data analysis.
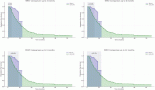
Results: No statistically significant differences were found in average outcome rates across the study period when grouped by radon exposure probability. Municipalities with higher exposure probabilities showed an increasing trend in lung cancer incidence and hospitalisation rates, while mortality remained stable. Additionally, hospitalisation rates increased in municipalities with lower exposure probabilities.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated the methodological challenges of investigating the association between gases and cancer etiology.