Background: The data on tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) promoter gene polymorphism in the African population are relatively limited, especially in Nigerian women.
Objectives: This study aimed to determine the prevalence and allele distribution of three TNF-α promoter gene SNPs loci – rs361525 (−238 G>A), rs1799964(−1031 T>C) and rs1800629 (−308 G>A) in women with cervical cancer (CC) and then evaluated the association between TNF-α SNPs and CC among women in Lagos, Nigeria.
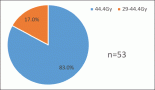
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study of 75 unmatched human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected and uninfected women with and without CC enrolled from October 2021 to January 2023 at the gynaecological oncology, cytology, adult HIV and blood donor clinics of the Lagos University Teaching Hospital. About 5 mL of peripheral blood was collected from each participant for total Deoxyribonucleic acid extraction, primer synthesis and genotyping. The probability of developing CC based on the given SNP genotype was expressed as an odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval. Allelic frequency deviations from Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium were calculated using chi-square, and the statistical significance level was considered as two-tailed and set at p ≤ 0.05.
Results: Our study found that TNF-α −1031 T>C polymorphism was significantly associated with increased CC risk in HIV-negative women (HIV+/CC-; OR = 1.4, 95%CI 0.23–8.42, p = 0.03 and HIV-/CC-; OR = 1.37, 95%CI 0.01–1.68, p = 0.03) while the −308A>G A allele was also significantly associated with CC in HIV-positive women (OR = 1.33, 95%CI = 0.23–7.75).
Conclusion: We observed that HIV-negative and HIV-positive women who carry the C allele of −1031T>C and the A allele of −308G>A TNF-a promoter gene loci, respectively, are more susceptible to CC. We were also able to show protective linkages for the minor allele of the three SNPs of interest suggesting the potential of TNF-a as a surrogate marker for CC screening in addition to human papillomavirus primary testing. Further studies are required to determine the association between host factors and TNF-a polymorphism to harness the diagnostic and therapeutic advantage these associations will provide in the management of CC.