Background: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors have shown significant efficacy in ALK -rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with good performance status (PS) in multiple randomised studies. However, there is limited data on patients with poor performance status.
Patients and methods: We carried out a retrospective analysis of prospectively collected data of patients with ALK-rearranged NSCLC and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) PS of 2–4 treated at a single academic cancer centre from January 2013 to November 2018. The outcomes, progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated from the date of diagnosis. SPSS version 20 was used for all statistical calculations.
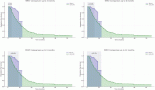
Results: Out of the total 441 ALK-positive patients, 97 (21.9%) had ECOG PS 2–4 (poor PS). The median PFS was 9.3 months (95% CI = 6.6–12.0) as compared to 14.9 months (95% CI = 13.4–16.4) for patients with a PS of 0–1 (HR = 1.38, 95% CI = 1.04–1.84, p = 0.027). The corresponding median OS were 17.9 months (95% CI = 12.8–23.1) and 33.5 months (95% CI = 28.6–38.4), respectively (HR = 1.89, 95% CI = 1.36–2.62, p < 0.001). Among poor PS patients, a subgroup of patients with PS 2 had median OS of 20.6 months (95% CI = 10.8–47.3) as compared to 8.6 months for PS 3–4 (95% CI = 7.8–27.8) (HR = 1.79, 95% CI = 1.01–3.20, p = 0.047). The patients treated with upfront ALK inhibitors had better survival as opposed to those treated with chemotherapy. On multivariate analysis, PS 3–4, smoking, stage 4 and not using ALK inhibitors as first-line therapy were associated significantly with poor outcomes.
Conclusion: The ALK-rearranged NSCLC patients with poor PS derived significant benefits with ALK inhibitors. The outcomes were significantly poorer as compared to patients with PS 0–1; the subgroup of patients with PS 2 had better outcomes as compared to patients with PS 3–4.